Tune a Pipeline
With the ASE framework, you can not only capture data from the Rover to debug it: you can also send data to the Rover to tune services during runtime. We'll explore how by tuning a Rover's speed in the Basic Autonomous Driving pipeline.

Elias Groot
Founding Member, Ex-Software Lead and Ex-Project Administrator
Prerequisites
- You are connected to the ASE network
- You have
roverctland Docker installed - The Rover is powered on and put on NXP cup tracks
- The Rover is calibrated
- The Basic Autonomous Driving pipeline is installed on the Rover
roverctl-webis started in debug mode
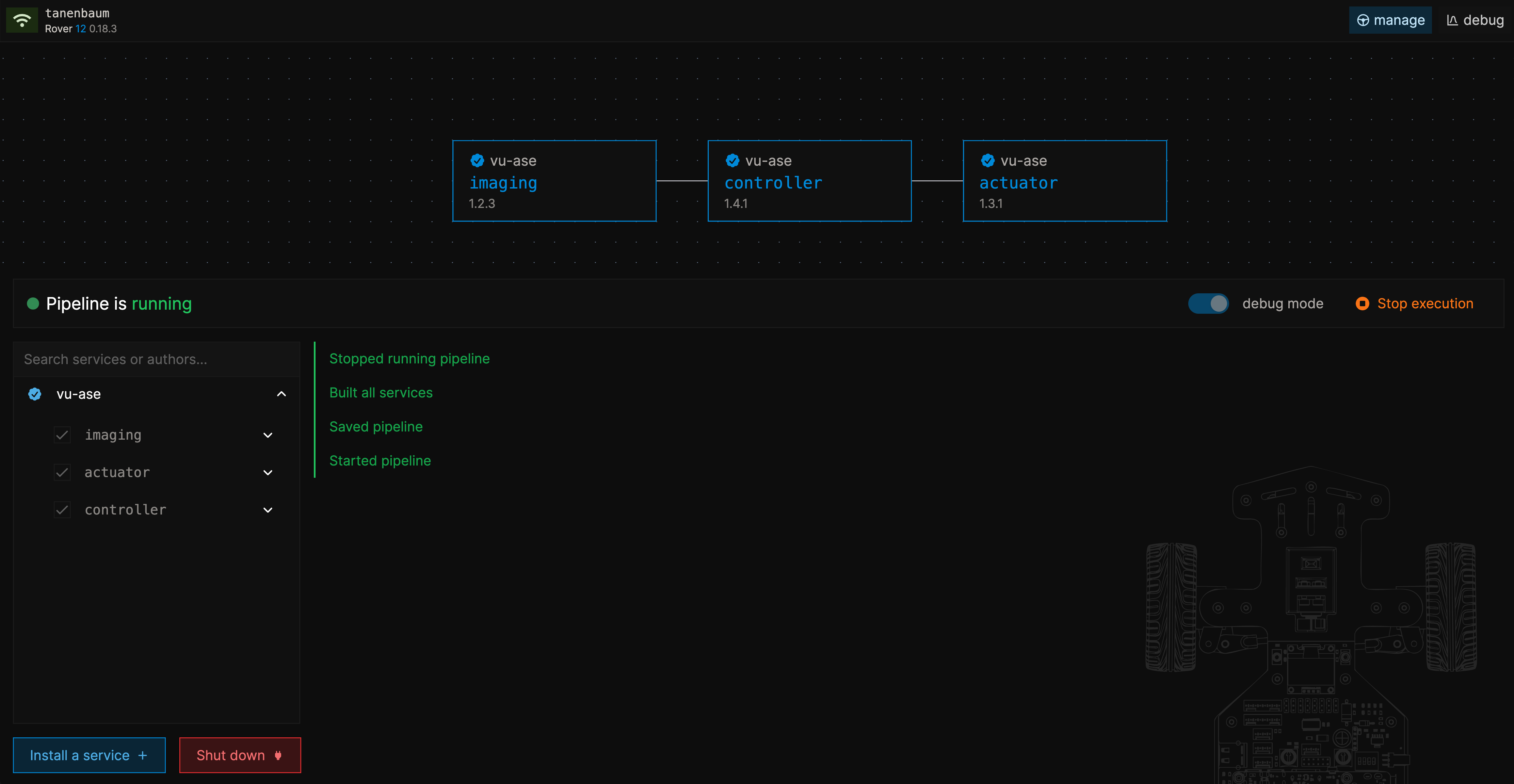
Set Up Your Pipeline
Enable the basic autonomous driving pipeline ("imaging", "controller" and "actuator") again on the manage page. and enable the debug mode toggle. Then press "start execution".
Send Tuning Information
Head over to the debug page using the navigation bar and expand the tuning tab of the controller service. You will be greeted with various variables and values.
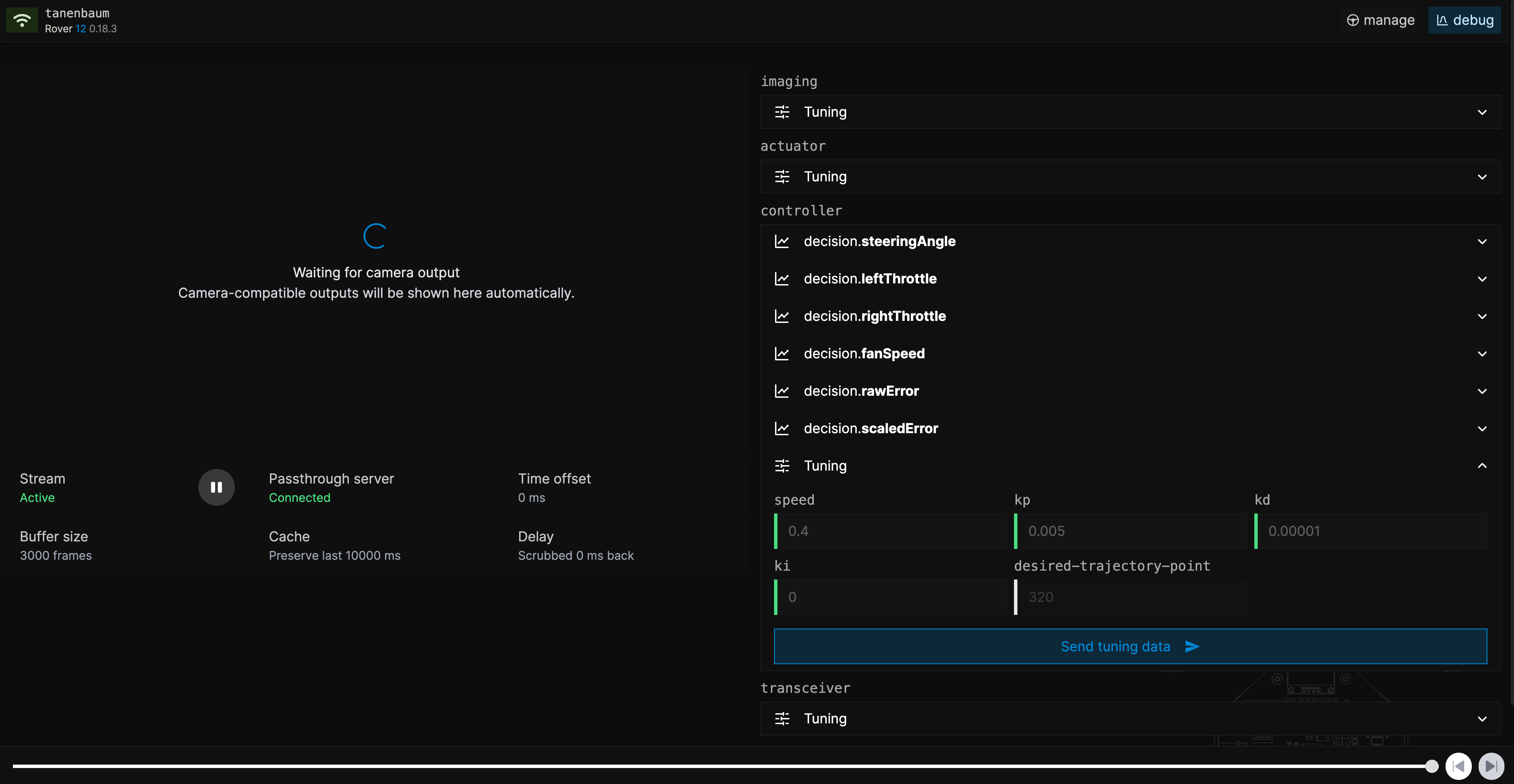
Values with a green edge can be tuned, unlike values with a gray edge, which will remain fixed for the entire lifetime of the pipeline.
Obviously, the speed value seems the most interesting one. Do not get tempted to go full speed now (remember the dangers). Let's try a slower speed first. Enter 0.2 to drive at 20% speed.
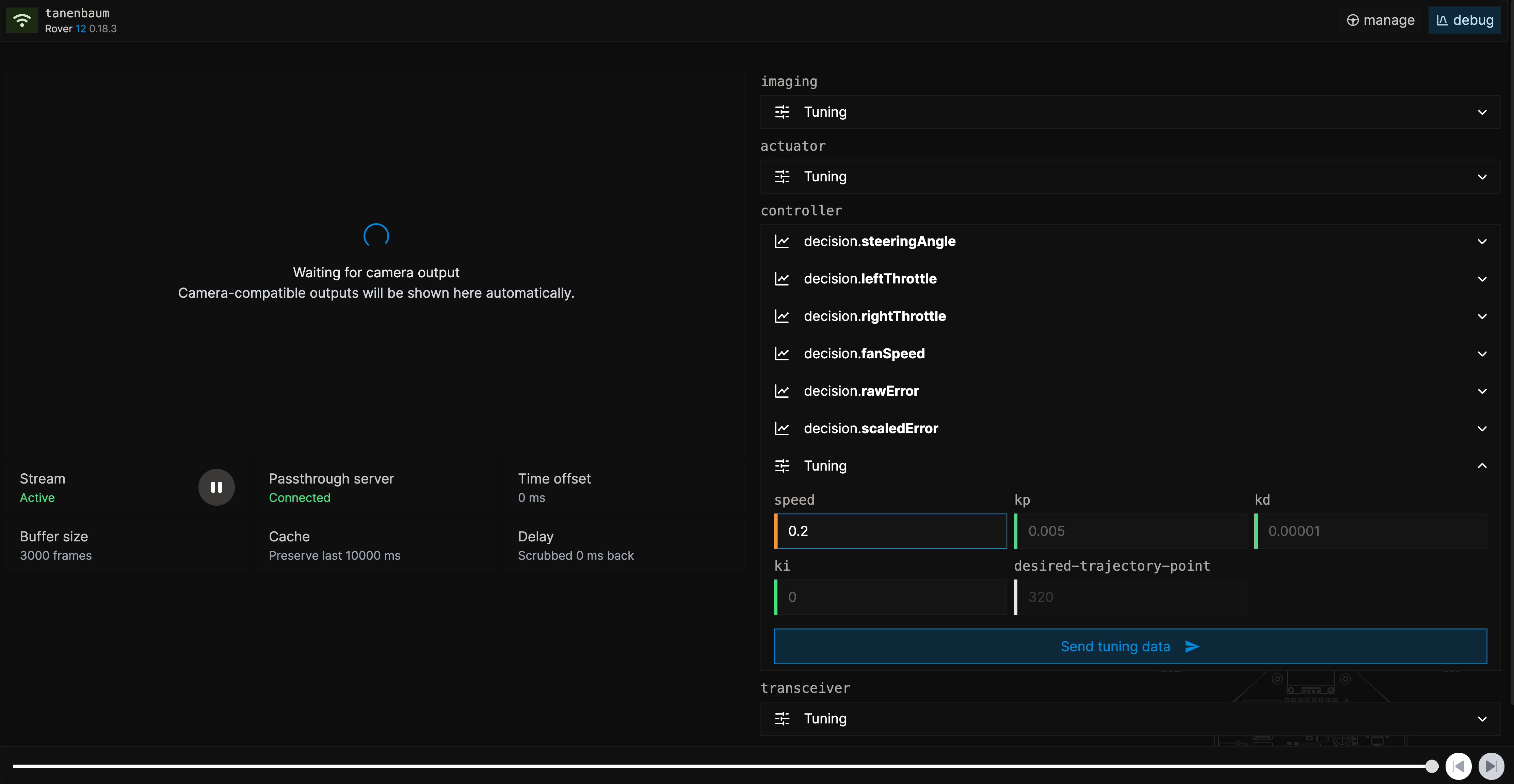
Notice that the value gets an orange edge, indicating that this tuning value has not been saved to the Rover yet. Double click "send tuning data" to save the data to the Rover to slow it down. Try to send 0.0 to fully stop the Rover.
Tuning options are available per service. You can try modifying them, but be aware that this might crash the Rover. Be ready to press ctrl/cmd + e to emergency reset the Rover.
Tuning is a powerful mechanism that is made possible by our service-oriented architecture. Tuning values are not persisted among pipeline restarts.